can ketoacidosis cause death Ketoacidosis pathophysiology dka euglycemic f6publishing windows hyperglycemia acidosis mellitus
Ah, diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), one of the common complications of diabetes that requires immediate attention. Let’s dive into its pathogenesis and pathophysiology to gain a better understanding of this condition.
Pathogenesis of Diabetic Ketoacidosis
When it comes to DKA, understanding its pathogenesis is crucial. In simplest terms, it occurs due to an absolute or relative insulin deficiency in the body. This deficiency causes various metabolic abnormalities, leading to the elevation of blood glucose levels and the production of ketones.
 The initiation of DKA can be attributed to various factors such as illness, infection, missed insulin doses, or certain medications. These factors contribute to the breakdown of fatty acids into ketones, which are acidic in nature. As a result, the blood becomes acidic, leading to the symptoms associated with DKA.
The initiation of DKA can be attributed to various factors such as illness, infection, missed insulin doses, or certain medications. These factors contribute to the breakdown of fatty acids into ketones, which are acidic in nature. As a result, the blood becomes acidic, leading to the symptoms associated with DKA.
Pathophysiology of Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)
Understanding the pathophysiology of DKA can shed light on the intricate mechanisms at play during this condition. It involves a cascade of events driven by insulin deficiency and the subsequent metabolic disturbances.
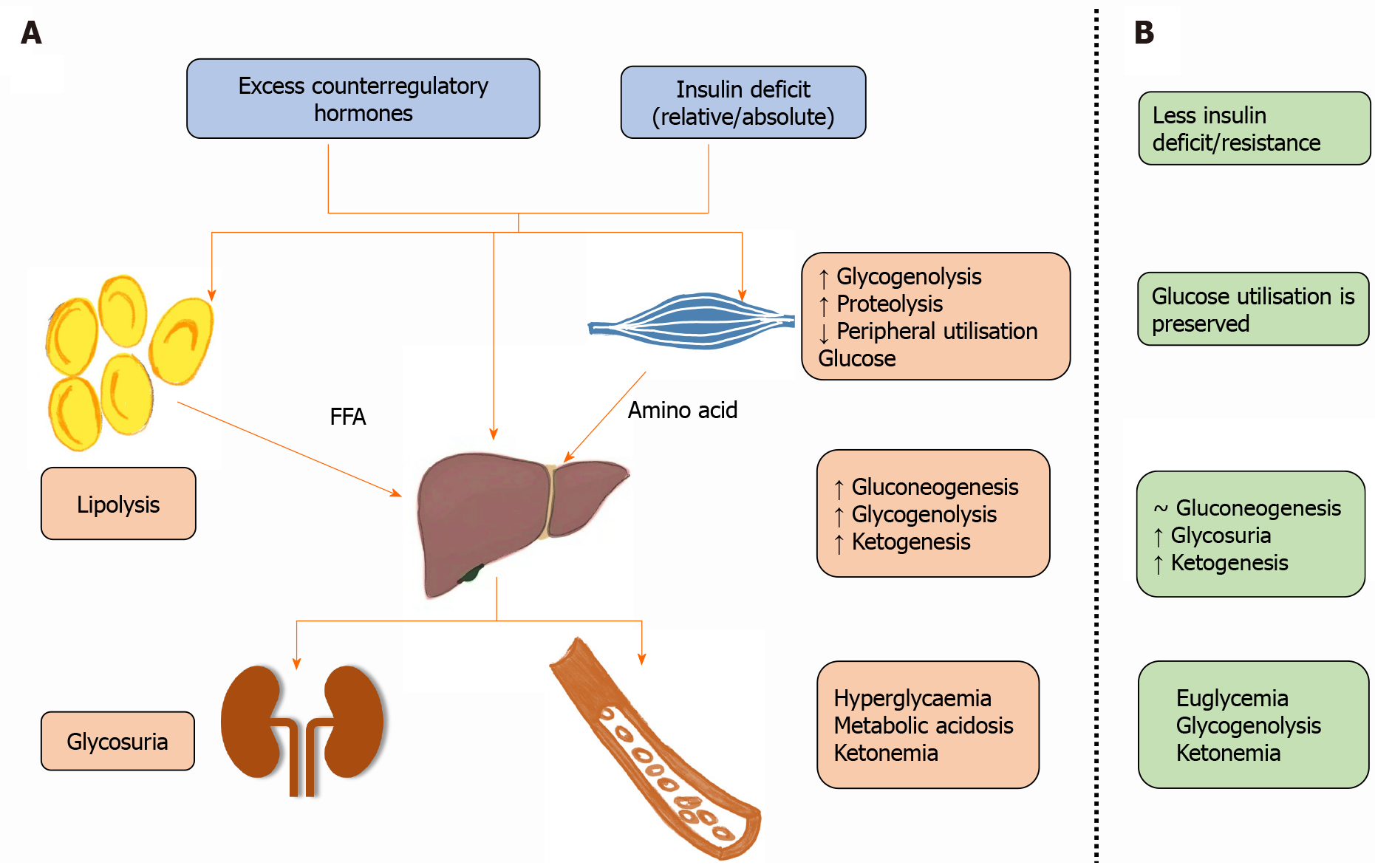 The lack of insulin prevents glucose uptake by cells, resulting in increased blood glucose levels (hyperglycemia). Subsequently, the body resorts to alternative fuel sources, such as fatty acids, for energy production. This leads to the breakdown of fatty acids into ketone bodies, including acetoacetate and beta-hydroxybutyrate.
The lack of insulin prevents glucose uptake by cells, resulting in increased blood glucose levels (hyperglycemia). Subsequently, the body resorts to alternative fuel sources, such as fatty acids, for energy production. This leads to the breakdown of fatty acids into ketone bodies, including acetoacetate and beta-hydroxybutyrate.
As ketone production increases, the equilibrium of acid-base balance in the body gets disrupted, resulting in ketoacidosis. The accumulation of ketones along with dehydration due to excessive urination leads to electrolyte imbalances, particularly potassium depletion.
The symptoms of DKA may include excessive thirst, frequent urination, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, fruity breath odor, and altered mental status. Without prompt medical intervention, DKA can progress to a life-threatening state.
It is important for individuals with diabetes to monitor their blood glucose levels regularly and adhere to their prescribed insulin regimen. Additionally, timely medical attention is crucial when experiencing any signs or symptoms of DKA.
In conclusion, DKA is a serious complication of diabetes that occurs due to insulin deficiency and subsequent metabolic derangements. Recognizing the pathogenesis and pathophysiology of this condition can help individuals better manage their diabetes and seek appropriate medical care when needed.
If you are searching about Pathogenesis of diabetic ketoacidosis | Download Scientific Diagram you’ve visit to the right page. We have 5 Pics about Pathogenesis of diabetic ketoacidosis | Download Scientific Diagram like Hyperglycemia DKA (Ketoacidosis) & Ketones - Diabetes - Innovation, Is Diabetic Ketoacidosis A Type Of Respiratory Acidosis - DiabetesWalls and also Learning About Ketoacidosis | Wellness Works NW. Here it is:
Pathogenesis Of Diabetic Ketoacidosis | Download Scientific Diagram
 www.researchgate.netketoacidosis diabetic pathogenesis
www.researchgate.netketoacidosis diabetic pathogenesis
Learning About Ketoacidosis | Wellness Works NW
 www.wellnessworksnw.comketoacidosis dka diabetic cetoacidosis deadly invokana coma
www.wellnessworksnw.comketoacidosis dka diabetic cetoacidosis deadly invokana coma
Is Diabetic Ketoacidosis A Type Of Respiratory Acidosis - DiabetesWalls
diabeteswalls.blogspot.comketoacidosis diabetic acidosis respiratory
Pathophysiology Of Diabetic Ketoacidosis / Diabetic Ketoacidosis Dka
 sraytguh.blogspot.comketoacidosis pathophysiology dka euglycemic f6publishing windows hyperglycemia acidosis mellitus
sraytguh.blogspot.comketoacidosis pathophysiology dka euglycemic f6publishing windows hyperglycemia acidosis mellitus
Hyperglycemia DKA (Ketoacidosis) & Ketones - Diabetes - Innovation
 danii.org.auketoacidosis dka hyperglycemia diabetic coma danii ketones passing serious
danii.org.auketoacidosis dka hyperglycemia diabetic coma danii ketones passing serious
Ketoacidosis dka hyperglycemia diabetic coma danii ketones passing serious. Is diabetic ketoacidosis a type of respiratory acidosis. Pathophysiology of diabetic ketoacidosis / diabetic ketoacidosis dka